 How do you pronounce the word "Apache"? What does it mean?Apache is pronounced "uh-PAH-chee." It means "enemy" in the language of their Zuni neighbors. The Apaches' own name for themselves was traditionally Nde or Ndee (meaning "the people"), but today most Apache people use the word "Apache" themselves, even when they are speaking their own language.
How do you pronounce the word "Apache"? What does it mean?Apache is pronounced "uh-PAH-chee." It means "enemy" in the language of their Zuni neighbors. The Apaches' own name for themselves was traditionally Nde or Ndee (meaning "the people"), but today most Apache people use the word "Apache" themselves, even when they are speaking their own language.
 Where do the Apaches live?The Apache are natives of the Southwest deserts (particularly in Arizona, New Mexico, and Texas). Some Apache people were also located across the border in northern Mexico. One Apache band, the Na'ishan or Plains Apache, lived far away from the other Apaches, in what is now Oklahoma. Their customs were different from other Apaches, more similar to their Kiowa allies. For that reason, the Americans often called the Na'ishan "Kiowa-Apaches." Here are some maps of the different Apache communities today.
The Plains Apaches are still living in Oklahoma today. Some Apaches from other bands were captured and sent to live in Oklahoma by the Americans in the 1800's, while other Apaches resisted being moved and remain in Arizona and New Mexico today. The total Apache Indian population today is around 30,000.
Where do the Apaches live?The Apache are natives of the Southwest deserts (particularly in Arizona, New Mexico, and Texas). Some Apache people were also located across the border in northern Mexico. One Apache band, the Na'ishan or Plains Apache, lived far away from the other Apaches, in what is now Oklahoma. Their customs were different from other Apaches, more similar to their Kiowa allies. For that reason, the Americans often called the Na'ishan "Kiowa-Apaches." Here are some maps of the different Apache communities today.
The Plains Apaches are still living in Oklahoma today. Some Apaches from other bands were captured and sent to live in Oklahoma by the Americans in the 1800's, while other Apaches resisted being moved and remain in Arizona and New Mexico today. The total Apache Indian population today is around 30,000.
Natural Resources
The Apaches home land consisted of plains, mountains, and hills.
Apaches natural resources were lakes, streams, rocks, minerals, timber, wildlife, and vegetation. They had diverse areas in which they would migrate around in. The Apache would follow the buffalo herd around these different areas. They would constantly come back to familiar areas.
Natural resources in the Apache area effected their culture for many reasons. A natural resource that effected their culture was lakes. Lakes supplied these native people's with water, meat, and plants. Hunting near lakes was a convenience because many animals came to drink from the lake. Water is necessary need for basic survival. Once Apaches figured out how to make flasks for water making a stop at lakes to refill on water was practical. Healthy vegetation grew near the banks of Apache lakes and they would collect the edible plants to eat. Apaches culture was Unique because of this resource. They built their technologies on this water source. Apaches people were able to fish and build their houses in a way that Native Americans without water could not. As a result Apache tribes built their culture and technologies on these natural resources.
 How is the Apache Indian nation organized?There are thirteen different Apache tribes in the United States today: five in Arizona, five in New Mexico, and three in Oklahoma. Each Arizona and New Mexico Apache tribe lives on its own reservation. Reservations are lands that belong to Indian tribes and are under their control. The Oklahoma Apaches live on trust land. Each Apache tribe has its own government, laws, police, and services, just like a small country. However, the Apaches are also US citizens and must obey American law.
In the past, each Apache band was led by its own chief, who was chosen by a tribal council. Most important decisions were made by the council, and all the Apache councilmembers had to agree before an action could be taken. An Apache chief was more like a tribal chairman than a president. Most of his job was mediating between other Apaches. Most Apache tribes still use tribal councils for their government today.
How is the Apache Indian nation organized?There are thirteen different Apache tribes in the United States today: five in Arizona, five in New Mexico, and three in Oklahoma. Each Arizona and New Mexico Apache tribe lives on its own reservation. Reservations are lands that belong to Indian tribes and are under their control. The Oklahoma Apaches live on trust land. Each Apache tribe has its own government, laws, police, and services, just like a small country. However, the Apaches are also US citizens and must obey American law.
In the past, each Apache band was led by its own chief, who was chosen by a tribal council. Most important decisions were made by the council, and all the Apache councilmembers had to agree before an action could be taken. An Apache chief was more like a tribal chairman than a president. Most of his job was mediating between other Apaches. Most Apache tribes still use tribal councils for their government today.
 What language do the Apache Indians speak?Almost all Apache people speak English today, but many Apaches also speak their native Apache language, which is closely related to Navajo. Apache is a complex language with tones and many different vowel sounds. Most English speakers find it very difficult to pronounce. If you'd like to know a few easy Apache words, "ash" (rhymes with 'gosh') means "friend" in Western Apache, and "ahéhe'e" (pronounced similar to ah-heh-heh-eh) means "thank you." You can read a Apache picture glossary here.
What language do the Apache Indians speak?Almost all Apache people speak English today, but many Apaches also speak their native Apache language, which is closely related to Navajo. Apache is a complex language with tones and many different vowel sounds. Most English speakers find it very difficult to pronounce. If you'd like to know a few easy Apache words, "ash" (rhymes with 'gosh') means "friend" in Western Apache, and "ahéhe'e" (pronounced similar to ah-heh-heh-eh) means "thank you." You can read a Apache picture glossary here.
 What was Apache culture like in the past? What is it like now?Here are the homepages of the Jicarilla Apache Nation and White Mountain Apache Tribe. On their sites you can find information about the Apache people from ancient times until today. You can also visit this site about the Apache Jii Festival, which has information and photographs about San Carlos Apache culture for kids.
What was Apache culture like in the past? What is it like now?Here are the homepages of the Jicarilla Apache Nation and White Mountain Apache Tribe. On their sites you can find information about the Apache people from ancient times until today. You can also visit this site about the Apache Jii Festival, which has information and photographs about San Carlos Apache culture for kids.
 How do Apache Indian children live, and what did they do in the past?They do the same things all children do--play with each other, go to school and help around the house. Many Apache children like to go hunting and fishing with their fathers. In the past, Indian kids had more chores and less time to play in their daily lives, just like colonial children. But they did have dolls, toys, and games to play. Apache children liked to run footraces and play archery games. Once the Apaches acquired horses, girls and boys as young as five years old learned how to ride. An Apache mother traditionally carried her baby in a cradleboard on her back.
How do Apache Indian children live, and what did they do in the past?They do the same things all children do--play with each other, go to school and help around the house. Many Apache children like to go hunting and fishing with their fathers. In the past, Indian kids had more chores and less time to play in their daily lives, just like colonial children. But they did have dolls, toys, and games to play. Apache children liked to run footraces and play archery games. Once the Apaches acquired horses, girls and boys as young as five years old learned how to ride. An Apache mother traditionally carried her baby in a cradleboard on her back.
 What were men and women's roles in the Apache tribe?Apache women were in charge of the home. Besides cooking and taking care of children, Apache women built new houses for their families every time the tribe moved their location. Though it was rare for an Apache woman to become a warrior, girls learned to ride and shoot just like the boys did, and women often helped to defend Apache villages when they were attacked. Apache men were hunters, warriors, and political leaders. Only men were chiefs in the Apache tribe. Both genders took part in story-telling, artwork and music, and traditional medicine.
What were men and women's roles in the Apache tribe?Apache women were in charge of the home. Besides cooking and taking care of children, Apache women built new houses for their families every time the tribe moved their location. Though it was rare for an Apache woman to become a warrior, girls learned to ride and shoot just like the boys did, and women often helped to defend Apache villages when they were attacked. Apache men were hunters, warriors, and political leaders. Only men were chiefs in the Apache tribe. Both genders took part in story-telling, artwork and music, and traditional medicine.
 What were Apache homes like in the past?Most Apache people lived in wickiups, which are simple wooden frames covered by a matting of brush and sometimes a buffalo-hide tarp. Wickiups were small dwellings, often the size of a modern camp tent, and an Apache woman could build a new wickiup in two hours if there was enough brush available. Here are some pictures of Indian brush houses. The Plains Apaches and some Lipan Apaches used buffalo-hide tipis as housing instead, which are more spacious and easier to heat than wickiups.
Apache people today do not normally use old-fashioned houses like a teepee or wickiup for shelter, any more than you live in a log cabin. Most Apaches live in modern houses and apartment buildings, just like you. However, some followers of the traditional Apache religion do live in modified larger wickiups, because their beliefs require them to burn down and rebuild their houses whenever there is a death in the family, which can't be done in an apartment.
What were Apache homes like in the past?Most Apache people lived in wickiups, which are simple wooden frames covered by a matting of brush and sometimes a buffalo-hide tarp. Wickiups were small dwellings, often the size of a modern camp tent, and an Apache woman could build a new wickiup in two hours if there was enough brush available. Here are some pictures of Indian brush houses. The Plains Apaches and some Lipan Apaches used buffalo-hide tipis as housing instead, which are more spacious and easier to heat than wickiups.
Apache people today do not normally use old-fashioned houses like a teepee or wickiup for shelter, any more than you live in a log cabin. Most Apaches live in modern houses and apartment buildings, just like you. However, some followers of the traditional Apache religion do live in modified larger wickiups, because their beliefs require them to burn down and rebuild their houses whenever there is a death in the family, which can't be done in an apartment.

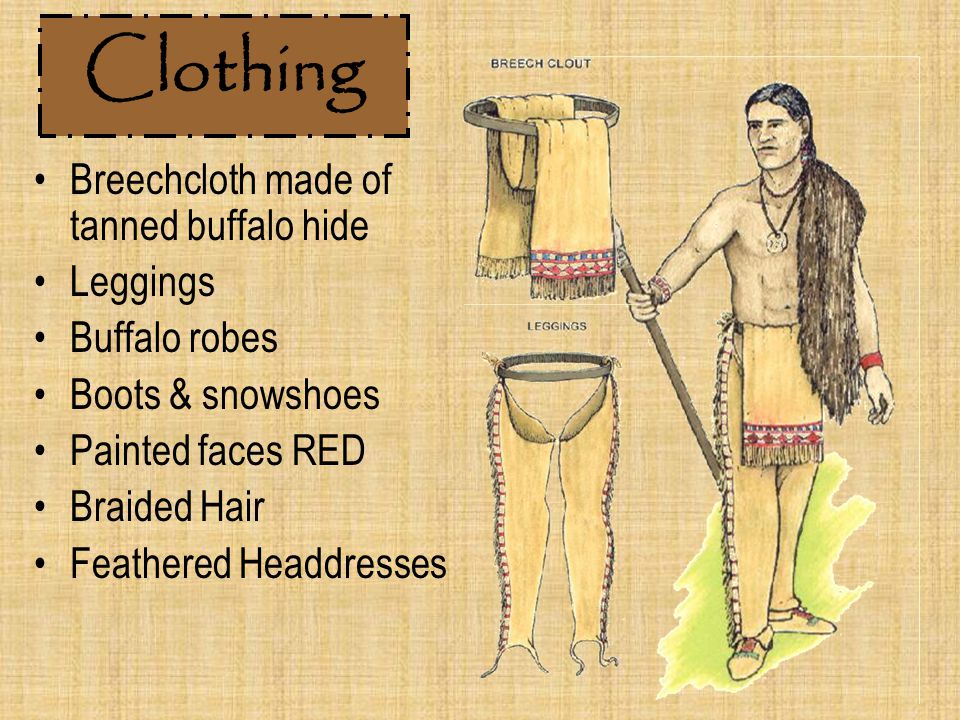
 What was Apache clothing like? Did the Apaches wear feather headdresses and face paint?Originally Apache women wore buckskin dresses and the men wore leather war shirts and breechcloths. In the 1800's, many Apache men started to wear white cotton tunics and pants, which they adopted from the Mexicans, and many Apache women wore calico skirts and dresses. The Apaches wore moccasins or high moccasin boots on their feet. An Apache lady's dress or warrior's shirt was often fringed and decorated with beaded designs. Here is a site about the symbolism of Plains Indian war shirts, and some photos and links about Indian costume in general.
The Apaches did not traditionally wear feather warbonnets, but the Plains Apaches adopted these headdresses from their friends the Kiowas. Other Apache people wore leather or cloth headbands instead. For ceremonies Apache people sometimes wore special wooden headdresses and masks, like these Apache Crown Dancers. Women usually wore their hair long and loose or gathered into a bun. Many young Apache women fastened their buns with hourglass-shaped hair ornaments called nah-leens. We haven't yet found a good photo of a nah-leen to share with you, but here is a photograph of some Caddo women wearing the same type of hair fastener. Apache men often cut their hair to shoulder length (except in the Plains Apache tribe.) Here is a website with pictures of these Indian hair styles. Both sexes liked to wear shell jewelry, especially choker-style necklaces. The Apaches also painted their faces for special occasions. They used different patterns for war paint, religious ceremonies, and festive decoration.
What was Apache clothing like? Did the Apaches wear feather headdresses and face paint?Originally Apache women wore buckskin dresses and the men wore leather war shirts and breechcloths. In the 1800's, many Apache men started to wear white cotton tunics and pants, which they adopted from the Mexicans, and many Apache women wore calico skirts and dresses. The Apaches wore moccasins or high moccasin boots on their feet. An Apache lady's dress or warrior's shirt was often fringed and decorated with beaded designs. Here is a site about the symbolism of Plains Indian war shirts, and some photos and links about Indian costume in general.
The Apaches did not traditionally wear feather warbonnets, but the Plains Apaches adopted these headdresses from their friends the Kiowas. Other Apache people wore leather or cloth headbands instead. For ceremonies Apache people sometimes wore special wooden headdresses and masks, like these Apache Crown Dancers. Women usually wore their hair long and loose or gathered into a bun. Many young Apache women fastened their buns with hourglass-shaped hair ornaments called nah-leens. We haven't yet found a good photo of a nah-leen to share with you, but here is a photograph of some Caddo women wearing the same type of hair fastener. Apache men often cut their hair to shoulder length (except in the Plains Apache tribe.) Here is a website with pictures of these Indian hair styles. Both sexes liked to wear shell jewelry, especially choker-style necklaces. The Apaches also painted their faces for special occasions. They used different patterns for war paint, religious ceremonies, and festive decoration.

 What was Apache transportation like in the days before cars? Did they paddle canoes?No--the Apache Indians weren't coastal people, and rarely traveled by river. Originally they just walked. There were no horses in North America until colonists brought them over from Europe, so the Apaches used dogs pulling travois (a kind of drag sled) to help them carry their belongings. Once Europeans brought the horse to America, the Apaches quickly became expert riders and could travel much more quickly than before.
What was Apache transportation like in the days before cars? Did they paddle canoes?No--the Apache Indians weren't coastal people, and rarely traveled by river. Originally they just walked. There were no horses in North America until colonists brought them over from Europe, so the Apaches used dogs pulling travois (a kind of drag sled) to help them carry their belongings. Once Europeans brought the horse to America, the Apaches quickly became expert riders and could travel much more quickly than before.
 What was Apache food like in the days before supermarkets?The Apaches were not farming people like their cousins the Navajos. Primarily they were hunters. Apache men hunted buffalo, deer, antelope, and small game, while women gathered nuts, seeds, and fruit from the environment around them. Although most Apache people were not farmers, the Apaches still used to eat corn frequently. They got it by trading with the Pueblo tribes and the Spanish, or by capturing it during raids. Favorite Apache recipes included cornbread and acorn stew.
What was Apache food like in the days before supermarkets?The Apaches were not farming people like their cousins the Navajos. Primarily they were hunters. Apache men hunted buffalo, deer, antelope, and small game, while women gathered nuts, seeds, and fruit from the environment around them. Although most Apache people were not farmers, the Apaches still used to eat corn frequently. They got it by trading with the Pueblo tribes and the Spanish, or by capturing it during raids. Favorite Apache recipes included cornbread and acorn stew.
 What were Apache weapons and tools like in the past?Apache hunters used bows and arrows. In war, Apache men fired their bows or fought with long spears and buffalo-hide shields.
What were Apache weapons and tools like in the past?Apache hunters used bows and arrows. In war, Apache men fired their bows or fought with long spears and buffalo-hide shields.
 What are Apache arts and crafts like?Apache artists are famous for their fine beadwork and basketry. Eastern Apache people sometimes made Southwestern pottery like the Pueblo Indians. Here is a website with many pictures of Apache baskets, and one about the history of Apache pottery.
What are Apache arts and crafts like?Apache artists are famous for their fine beadwork and basketry. Eastern Apache people sometimes made Southwestern pottery like the Pueblo Indians. Here is a website with many pictures of Apache baskets, and one about the history of Apache pottery.



 What is Apache Indian music like?Music is very important to Apache Indian culture. There are different types of traditional Apache songs for ceremonial, social, and entertainment purposes. Singing together in the Apache language is the most important part of Apache music, but musical instruments such as drums, flutes, and rattles are also used. Drums and rattles are especially used during dances, while flutes are particularly associated with love songs. Some Apache groups also played a sort of fiddle made out of agave stalks.
What is Apache Indian music like?Music is very important to Apache Indian culture. There are different types of traditional Apache songs for ceremonial, social, and entertainment purposes. Singing together in the Apache language is the most important part of Apache music, but musical instruments such as drums, flutes, and rattles are also used. Drums and rattles are especially used during dances, while flutes are particularly associated with love songs. Some Apache groups also played a sort of fiddle made out of agave stalks.
http://www.bigorrin.org/apache_kids.htm
Religious Beliefs.In traditional belief, a Creator (neither male nor female), which is beyond human comprehension but is manifested in natural phenomena, made the world in four days. Portions of the Creator may be seen in the natural universe (thunder, wind, and so on), and the physical representation is said to be the sun. In addition, there are two Culture heroes, the Twin War Gods, Born for Water and Killer of Enemies, as well as a heroine, White Painted Woman. Power suffuses the universe and can be employed for good or ill. There are now many Christian denominations on the reservation; most people compartmentalize and maintain both Religious systems.
Read more: https://www.everyculture.com/North-America/Mescalero-Apache-Religion-and-Expressive-Culture.html#ixzz5U7kkLzyn
https://apacheblackfootcomparrison.weebly.com/natural-resources.html





